Presentation Information
[O9-4]Effect of Mn doping on the synthesis and properties of nearly spherical Sm2Fe17N3 powders
Pengfei Yue1, Dongsheng Shi1, Jingwu Zheng1, Wei Cai1, Liang Qiao1, Yao Ying1, *Shenglei Che1 (1. Research Center of Magnetic and Electronic Materials, College of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou 310014, China (China))
Keywords:
Sm-Fe-N,Mn doping,Ultrasonic spray pyrolysis,magnetic particle
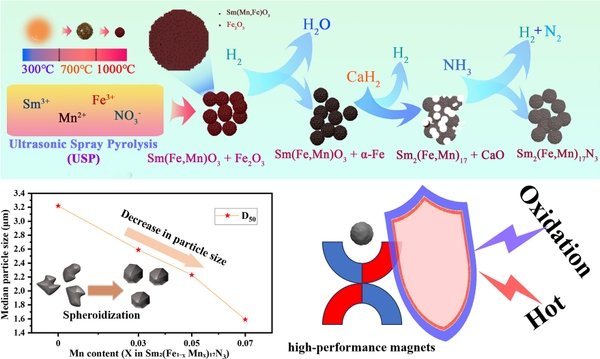
To achieve smaller particle sizes of Sm2Fe17N3 magnetic powders, crushing is often applied to the obtained powders. However, this process introduces more angular edges and increases the risk of oxidation. In this study, nearly spherical Sm2(Fe,Mn)17N3magnetic powders with controllable particle sizes and strong oxidation resistance were prepared eliminating the need for crushing, using a combined ultrasonic spray pyrolysis-reduction diffusion method. The results show that appropriate Mn doping facilitates particle size refinement. Mn substitution of Fe increased lattice expansion without altering crystal structure. The optimal coercivity occurred at a 5 at.% Mn substitution. Furthermore, as the Mn doping level increased, the proportion of adsorbed oxygen decreased, slowing the occurrence of further oxidation reactions and impeding the transformation of metallic elements into higher-valence oxides, thereby enhancing oxidation resistance. The addition of Mn improved the thermal stability and magnetic properties of Sm2Fe17N3magnets, offering a promising method for producing high-performance permanent magnets.