Presentation Information
[R1-P-19]Lindbergite from the Taguchi mine, Aichi Prefecture, Japan
*Masayuki Ohnishi, Norimasa Shimobayashi1, Keiji Shinoda2, Daisuke Nishio-Hamane3, Takeshi Hisano (1. Sci., Kyoto Univ.Kyoto Univ., 2. Sci., Osaka Metro. Univ., 3. ISSP, Univ. of Tokyo)
Keywords:
Lindbergite,Oxalate,Organic mineral,Taguchi mine,Manganese deposit
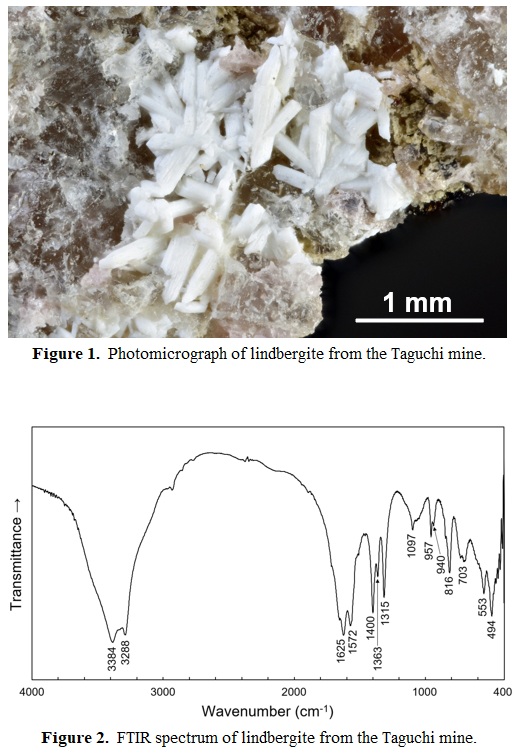
Lindbergite was found from the stratiform manganese deposit of the Taguchi mine, Shitara, Aichi Prefecture, Japan. The mineral rarely occurs as aggregates of prismatic crystals up to 1 mm in length and 0.2 mm in wide in crack of quartz-rhodonite-“biotite” assemblage. It is translucent and is white in color with a vitreous luster (Fig. 1). The measured density is 2.28(1) g cm-1. The unit cell parameters refined from the powder X-ray diffraction data are a = 12.04(1), b = 5.646(2), c = 9.97(1) Å, β = 128.02(7)°, and V = 533.9(17) Å3. FTIR spectrum (KBr method) shows the absorptions bands of O-H stretching (3384 and 3288 cm-1), H-O-H bending (1625 cm-1), O–C–O antisymmetric stretching (1572 cm-1), O–C–O symmetric stretching (1400, 1363 and 1315 cm-1) and Mn-O stretching (816 cm-1), respectively (Fig. 2). SEM-EDS analysis yields the empirical formula (Mn0.973Mg0.024Ca0.003)Σ1.000 (cationic part only) on the basis of total cations = 1.